Immediate action required. Control Panel – Windows Update – Check for Updates. Adobe also released important patches.
Also update Power Query – the Excel add-in which helps you get and clean data. Many new features and enhancements are added…
Windows Update, Adobe Update, Power Query Update
Contents
Windows update
Read this article for details about why you should always apply updates promptly after they are available. Are you applying updates to Windows and Office?
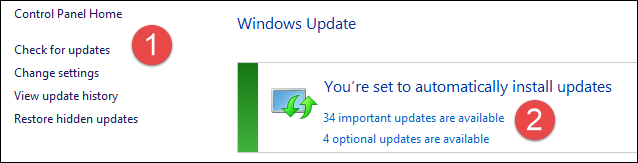
For now, just go to Control Panel – Security – Windows Update – Click on Check For Updates
Click on the important updates link and apply. In your case the number may not be 34. It depends upon which version of Windows and Office you are using. It also depends upon many other hardware factors as well. So don’t worry about the number. Just install all those which are important.
This time many patches were added. The size of the patches could be significant – in my case it was almost one GB. Therefore, make sure that you have a good connection while patches are being downloaded.
Adobe Patches
Adobe also has an updater which should be set to automatic update mode. The concept is absolutely similar to windows updates. If you have Adobe CC subscription, the updates will happen through it. If you have installed individual Adobe products, there is a separate Adobe Update application. Configure it to manage automatic updates.
Even if you have not purchased any specific Adobe product, it is very likely that you will have Flash and Adobe Acrobat Reader installed. These products are also very commonly targeted by hackers. Therefore, updating them is as important as keeping Windows up-to-date. You can also download the May 2014 patches from here.
Power Query Update
I was going to write this as a separate post. However, these three patches coincided. Hence it is a single article. Power Query update was released on 5th May. It is more about feature enhancements rather than bug fixes and security.
Download the update from here. Read the announcement on Microsoft BI blog. Once installed, check the version in PowerQuery ribbon – About. It should be 2.11.3625.144.
Here are the useful new additions.
Tables and Named ranges
This is the most important change. Excel continues to be a common date source. However both Power Query and Power Pivot only accepted sheets as inputs. Due to this, more than one blocks of data in one sheets were impossible to manage.
Another problem was that if the data did not start at A1, extra clean up steps were required. The solution was to allow importing Tables and Named Ranges rather than sheets. Now it is possible.
Referring to an Excel file shows the available Tables and named items. You can choose what you want from the Navigator.
Mouse hover also shows a preview (Peek) as well.
Right click on the desired item and choose Edit.
Earlier, the peek showed the Edit button, which is now removed. Now it is available in the right click menu as well as at the bottom of the Navigator pane.
Access
Yes. There are many of you out there who still use Access. Now you can connect to Access tables. Having said that, remember that the most common reason we used to need Access is to handle the row limits of Excel. Another reason was to create relationships between primary, foreign key – create a query and then get combined output – this was a workaround for Vlookup.
If you are still using Access for these reasons, you must migrate to PowerPivot now. This is a much more sophisticated and optimal method from an operational, performance as well as capability point of view.
Calculated columns and formatting preserved
Once data is imported and loaded into Worksheet, we need to add calculated columns, conditional formatting, apply specific styles. These were overwritten after a refresh. Now the problem is solved. All this is preserved and managed intelligently after a refresh.
Similarly, many more convenient changes are incorporated in the new version of Power Query.
Where to load the data
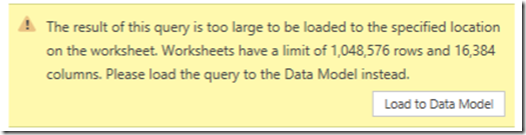
Power Query allows you to load the data into a worksheet or into Power Pivot Data Model. Single query output goes to worksheet by default and multiple output queries go to Data Model. However, if the output has more rows than what Excel can handle- it should be loaded into Data Model – which is what happens now. It provides a warning and changes the output destination to Data Model.
You can also change the defaults if required.
In general, try to use data model unless you have a very specific reason to use Worksheet based data. Data model compresses the data significantly, gives you more features and improves performance of Power View and Pivot Tables.
Remove Top / Bottom rows
Unwanted or empty rows at the top is a common scenario which was covered already. Removing bottom rows is added now. The bottom rows which are unwanted contain grand totals, footer information, summary and so on. These are beyond the usable end point of tabular data and therefore must be removed. Now it is possible with a single command.
That’s all in this article. In the next article, I will cover the Fill Up / Down feature of Power Query. It is a very powerful function – deserves detailed discussion – because it solves a very common problem very elegantly.
***